Quick Fixes for Office 365 Slowing Down the Computer
Office 365 slow performance issues can be a headache for employees in your organization and for customers. If Microsoft Office 365 slows down users’ computers, productivity suffers and workflows are disrupted. Customers may be dissatisfied accessing a slow SharePoint site, which would negatively impact your organization’s reputation. In this case, you should find the reasons for Office 365 performance issues and fix them as quickly as possible.
Why Is Office 365 Running Slow?
Multiple factors can cause Office 365 slow performance. These can include issues on a client’s computer (hardware and software), network or internet connection issues, and issues on Microsoft’s side (software updates, issues in a datacenter).
Internet Connection Issues
The main requirement for using Office 365 is an internet connection with high bandwidth and low latency. When using Office 365 online applications in a web browser and working with files in the cloud, a slow internet connection with high latency causes lag and delays. These Office 365 issues are inconvenient when you want to open a document or make changes, and can considerably slow down operations.
Fixing internet connection issues affecting Office 365 performance
- Check the configuration on your routers and firewalls. Ensure IP addresses, protocols and file types needed to work in Office 365 are not blocked.
- Make sure your router and firewall don’t terminate long-term TCP connections if they are idle. Office 365 establishes a high number of longer-lasting network connections. Check TCP idle time settings. Outlook Online initiates such connections for proper work.
If traffic shaping is configured, make sure the internet speed for clients is enough to work in Office 365. Network congestion reduces Office 365 performance, and traffic inspection software on routers also negatively impacts performance.
- Opt for a wired network over a wireless network connection. A wireless network connection can be unstable and have high latency. If you need to use a wireless connection, ensure that the signal level is strong enough, and the channel is selected correctly and doesn’t interfere with the same channel number of nearby Wi-Fi networks.
- Consider the round-trip time (RTT), which is the time it takes data to be sent from a sender to a destination host, plus the time needed to receive the acknowledgment back to the original sender. This time depends on the distance, transmission medium, the number of hops (routers), and the destination server’s response time.
- Check whether your internet connection is reliable and not interrupted. Lost packets negatively impact Office 365 performance. The easiest way to check network connection latency and stability for initial analysis is to ping Microsoft servers. It is recommended that local internet egress be made at the user’s location.
- Make sure DNS is configured and works correctly. Microsoft datacenters are distributed across the globe. Local computers should be connected to the nearest Microsoft datacenter to reduce the round-trip time and improve the user experience. Proper DNS configuration helps you achieve this. If your organization has a complex structure with branches in different countries or regions, configure local DNS servers at each branch location instead of using one central DNS server. Use the same approach to configure routing for internet access in branch offices.
- Check TCP window scaling configuration. Office 365 uses the TCP/IP stack to connect to Microsoft servers. Transport Control Protocol (TCP) is the protocol designed to track how much data has been transmitted with the guarantee of data transmission (unlike UDP). TCP flags or flag bits in a TCP header are used to initiate connections, carry data, and close connections. In this case, we are interested in SYN (synchronization) and ACK (acknowledgment) flags.
Note: How does a TCP connection using SYN and ACK flags work?
- SYN flags are used to initiate a connection. ACK flags acknowledge that the recipient has received a TCP segment successfully (confirm that the data has been received). A three-way TCP handshake with SYN and ACK flags establishes TCP connections.
- When you start a new TCP connection, hosts use a receive buffer where the data is temporarily stored until an application processes it. TCP windowing is when a sender sends one or multiple TCP segments, and a recipient acknowledges receiving one or all of these segments. A recipient sends the acknowledgment information about how much data a sender can transmit before the recipient sends an acknowledgment. The number of TCP segments (with the carried data) sent before getting an acknowledgment is known as the window size. The TCP connection usually starts with a small window; after each successful acknowledgment, the window size increases.
- Once an IP packet is dropped, the TCP window size is reduced back to one segment and begins to grow again. If a receive buffer is full, the window size is set to 0 until the buffer is freed up.
- The window size is originally a 16-bit value (65535 is the maximum corresponding decimal value), which is the size of a buffer in TCP headers. This 16-bit buffer fills in milliseconds, and then the delay occurs because traffic cannot be sent until the recipient sends an acknowledgment to the sender.
Nowadays, the 16-bit receive buffer and the appropriate maximum TCP window size can be increased by using a scaling factor. If a recipient cannot process the receive buffer in time and you notice delays, try to increase the buffer. You may need to use a network sniffer (traffic analyzer) to investigate the issue.
- Check the TCP maximum segment size. This is the maximum amount of data that can be carried in a TCP segment. TCP maximum segment size should not be less than 1460 bytes for optimal performance.
- You may need to upgrade your internet plan. For example, if you use 10-Mbit internet, transfer to 100-Mbit internet. In this case, you need to contact your internet service provider (ISP). It can help you fix problems with Office 365. If you use ADSL internet, keep in mind that the upload speed is much lower than the download speed due to ADSL’s asymmetric working principle. Using cable internet via twisted pair or fiber optic cable is better. Read more about network topology types in our guide.
- If you edit Word, Excel, and PowerPoint documents but don’t collaborate with other users online, consider installing Office 365 applications on your computer instead of using browser versions of Office 365 online apps. Save files on a local disk on your computer instead of saving files in OneDrive in the Office 365 cloud. With this approach, you won’t need to use an internet connection as much to work with Office 365 documents, and you can mitigate Office 365 issues related to network connections. Even if you store documents in a shared folder accessed via the local area network, the time needed to read and write MS Office documents is increased.
Software Issues
Another category of issues that can cause Office 365 performance degradation has to do with software. Software issues usually occur on a client’s computer. If you notice Office 365 slow performance, try to check software issues on your computer and fix the problems found. Ensure there are no software conflicts.
How software conflicts slow down Office 365
Software conflicts may occur when multiple applications are working and one application (Word, Excel, PowerPoint and other Office applications in this case) “interferes” with another one or with the system, and there is a competition for hardware resources. Software conflicts can slow down Office 365 applications.
Software conflicts can occur in the following situations:
- Two or more programs try to access the same resources.
- An application modifies or blocks services or processes used by another.
- Add-ins or plugins are outdated and their behavior is incorrect.
Having multiple versions of Microsoft Office (such as Office 2013 + Office 365) installed on the same system can cause confusion in file associations and plugin loading.
Fixing software issues affecting Office 365 performance
- Use antivirus software. Viruses and malware can consume CPU and memory resources for their malicious activity and, as a result, there won’t be enough hardware resources for the applications. In addition, ransomware can corrupt all data on your computer and other computers connected to your network.
Pro tip: Download our white paper and find out how to protect your data against ransomware.
- Computers infected with malware can generate parasitic traffic. You may need to check network traffic on a switch or router to detect the computer generating unwanted traffic.
- Make sure your antivirus software is configured properly. Some antiviruses can consume too many resources to check memory, network, and disk activity. Such behavior causes delays and performance degradation.
- Consider using Office 365 Advanced Threat Protection and Exchange Online Protection to reduce the risks of being infected with malware and ransomware via Office 365 email.
- Try closing unused applications except for the web browser for opening Office 365 online apps. Close other tabs in the browser and leave only those with open Office 365 applications. Check whether these operations helped fix issues.
- Disable add-ons and plugins in a web browser to check whether they have an impact on the performance of Office 365 online apps.
- Remove unused applications from the Windows startup configuration. They can cause conflicts with Microsoft Office 365 applications.
- Disable telemetry in Windows. Telemetry doesn’t provide useful features but consumes system resources to collect and send data to external hosts. It is always better to disable telemetry.
- Check Windows Registry for errors. Corrupted registry entries or user profiles affected by other software can cause delays in Office 365 startup or response.
Hardware Issues
If recommendations from previous sections have not helped you fix Microsoft Office 365 issues related to slow performance, check your hardware.
Fixing hardware issues affecting Office 365 performance
- Make sure your computer’s hardware meets the minimum requirements of Office 365. You can check system requirements on the Microsoft website.
- Check whether your disk drive is healthy. Bad blocks and blocks with high access time on a hard disk drive cause performance degradation and risk of data loss. Run the S.M.A.R.T. data test to identify disk issues and run disk surface tests if needed. Ensure there is enough free disk space on your system disk and the disk on which your browser and Office 365 applications are installed.
- Check whether your computer has enough RAM (Random Access Memory) and free memory. If not, the OS and application performance can degrade significantly. The operating system uses the swap file to perform many read/write operations when there is no available free memory.
Note: System monitoring can help you react quickly and avoid hardware issues causing low performance and possible data loss.
Why Is Outlook Running Slow?
In this section, we explain how to speed up Outlook. If you use a standalone version of Office 365 Outlook installed on your computer and notice significant performance issues, try performing the actions explained below.
Symptoms:
Email folders such as Inbox, Sent, Junk emails, etc. are opening slowly. If there are no internet connection issues for data synchronization in the email client, you may exceed the number of items per folder in one of these email folders. A similar issue may happen with a Calendar that doesn’t display the most recent items.
Solution:
Try to perform these actions to fix the issue when Outlook opens slowly.
- Delete items from the appropriate email folders.
- Configure Office 365 retention policies and set how long items must be stored.
- Enable the Exchange Online Archive Mailbox and configure email archiving to save space in your mailbox folders.
- Change the number of months for which data is synchronized for shared calendars in Sync Windows Settings.
- Update the installed Outlook application.
How to Fix SharePoint Performance Issues
- Use a free SharePoint Page diagnostics add-on for Google Chrome to check website page issues in SharePoint. This diagnostics tool can help you identify performance issues and factors that negatively impact performance.
- Reduce image resolution and compress images before uploading them to your SharePoint site’s web pages. Large images can slow down site performance and consume more internet traffic to load.
- Use the modern SharePoint interface instead of the classic one. The modern interface is better optimized for large sites to meet today’s requirements.
- It is recommended that you don’t use too many web parts on a single SharePoint web page. Using too many parts causes a SharePoint site’s web page to perform poorly. If you use iframes to display external content, don’t use too many (the recommendation is three or fewer).
Pro tip: Back up SharePoint Online data to have the ability to restore data in case of unexpected SharePoint Online issues.
Fixing Microsoft Word and Excel Running Slow Issues
Editing the settings of Office 365 applications, including Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, can increase their performance on your computer. The needed Microsoft Office application settings are located in File > Options. We use Word in our example, but the settings in Excel and PowerPoint are similar.
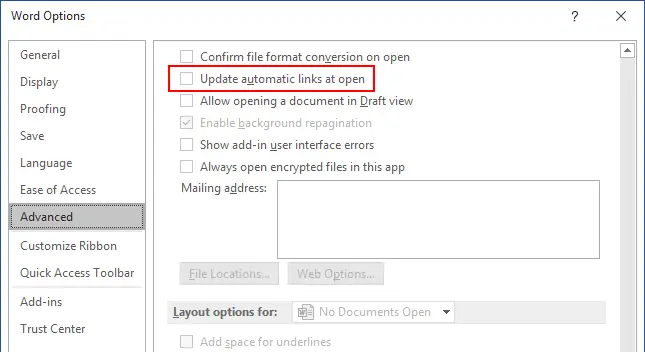
Disable updating automatic links when opening a document
Automatic links are used to link objects (tables, diagrams, images, etc.) in other source documents with the current document. Content changes in a source document are reflected in your current document where the active link is inserted. Automatic links can be a reason why Microsoft Word is slow.
To disable automatic links:
- Go to File > Options in Microsoft Word.
- Select the Advanced option in the Navigation pane.
- Deselect the Update automatic links at open checkbox.
- Hit OK to save settings and close the window.
Disable add-ins
Add-ins are small programs that can expand Word’s functionality. Enabled add-in components are loaded during Word startup, increasing the time it takes to open the application and making Microsoft Word run slowly.
To disable Add-ins:
- Go to File > Options in Microsoft Word.
- In the Word options window, click Add-Ins.
- Select COM Add-ins in the drop-down menu and click Go.
- Deselect checkboxes for the add-ins you want to disable.
- Hit OK to save settings.
You can run an Office 365 application in safe mode – add-ins are disabled in safe mode.
Run Outlook /safe or winword /safe from the Run dialog.
After opening an application in safe mode, you can disable add-ins (see a section below).
Adjust security settings
Editing some security settings can increase Word’s performance.
- Click File > Options in Microsoft Word.
- Select Trust Center in the Word Options window.
- Click Trust Center Settings.
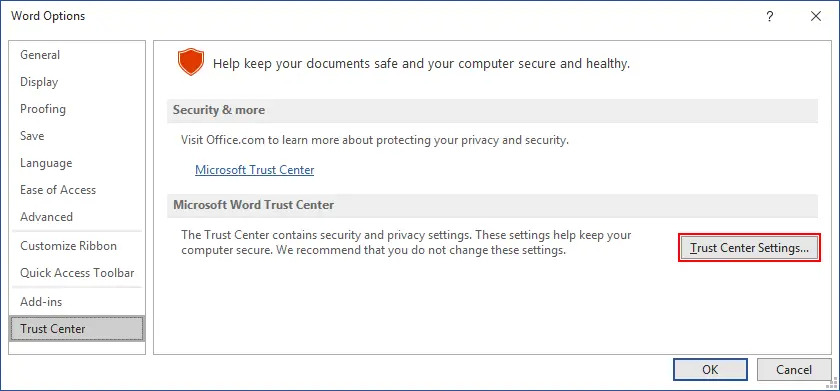
Be careful when you edit security settings if you don’t want to have Microsoft Office 365 security issues.
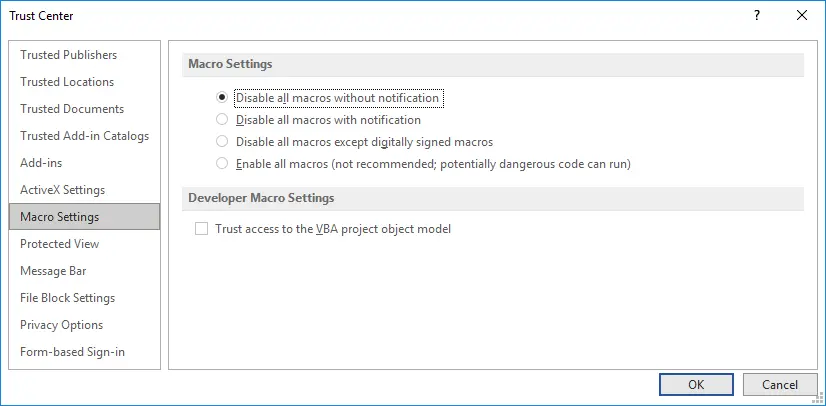
Disable macros
Macros from downloaded documents can constitute a threat. Running macros can initiate infecting a computer with ransomware (learn more about methods to detect ransomware in our post). When you open a document, checking a document for macros consumes resources before displaying a notification about the presence of macros in the document. If you don’t use macros in your documents, you can disable macros in Word settings.
To disable macros:
- Select Macro Settings in the navigation pane of the Trust Center window.
- Select Disable all macros without notification.
- Hit OK to save settings and close the window.
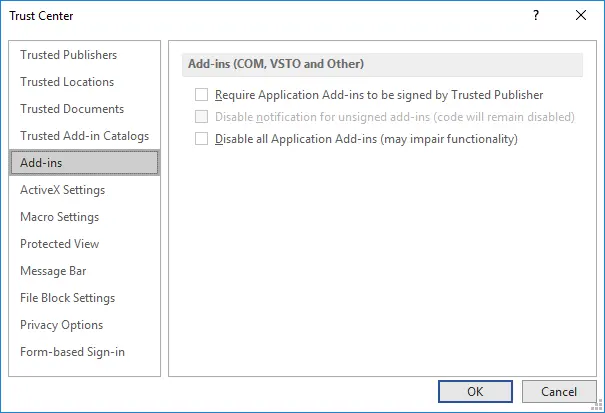
How to disable all add-ins
You can disable all add-ins in Trust Center:
- Click Add-ins in the Trust Center window.
- Select the checkbox Disable all Application Add-ins.
Fixing Issues when Microsoft OneDrive Slows Down the Computer
Microsoft Office 365 OneDrive performance issues can have different symptoms: a processor on your computer is too busy, the OneDrive process consumes too many CPU resources, the time to synchronize small amounts of data is high, etc. This section explains possible solutions to fix issues by editing settings in Windows and the OneDrive Sync client.
Restart the OneDrive application
You can perform the following steps to restart OneDrive:
- Press Win+R, type
taskmgrand press Enter to open the command prompt. - In the Processes tab, locate the Microsoft OneDrive process.
- Right-click this process and in the context menu, click End task.
- Restart your OneDrive Application. You can restart a computer and then restart OneDrive.
Stop file synchronization
File synchronization is a possible reason why OneDrive slows down a computer. You can put synchronization on pause and verify whether your computer works faster after that.
- Right-click the OneDrive icon in the Windows system tray (in the bottom right corner near the clock).
- In the context menu, click Pause syncing and select the time (2, 8 or 24 hours).
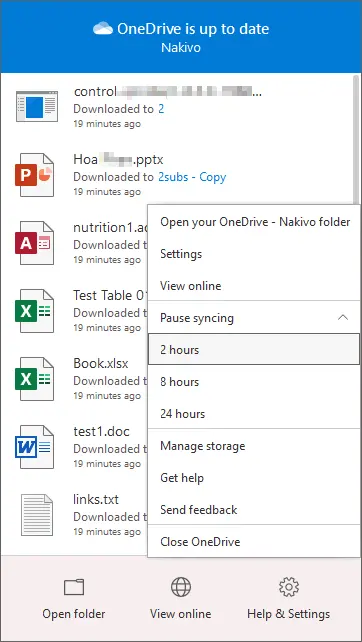
- Check whether the performance of your computer has improved.
If you notice that performance is better, it means that OneDrive synchronization is slowing down your computer.
Unlink OneDrive
If you still notice that OneDrive slows down a computer, try to unlink the OneDrive application from the computer.
- Open the window of the OneDrive application installed on your computer.
- Click the Help & Settings icon.
- Click Settings in the opened menu.
- In the Account tab, click Unlink this PC.
- Hit OK to save settings and close the window.
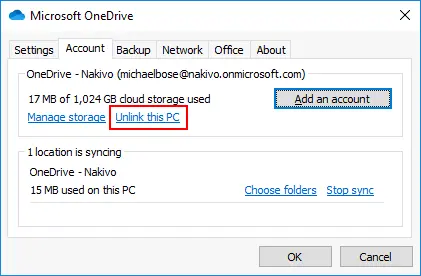
- Wait until the unlinking process is finished.
- Start OneDrive Setup Wizard and follow standard instructions.
- Set up a new folder on your computer for OneDrive synchronization.
Note: Make sure this folder is located on a healthy disk drive.
- Copy or move files from the old OneDrive folder to the new one.
- Check whether the OneDrive issue has been fixed.
Remove OneDrive from Windows startup
Removing OneDrive from automatic startup after the Windows boot can help you avoid Microsoft OneDrive slowing down a computer right after the OS starts until you research and fix the issue. This approach allows you to get normal performance on a computer while allowing you to run OneDrive manually. After resolving OneDrive performance issues, you can add OneDrive to Windows startup.
Follow these steps to remove OneDrive from Windows 10 startup:
- Right-click Start or the taskbar and in the context menu, click Task Manager.
- Locate Microsoft OneDrive in the Startup tab of the Task Manager window.
- Right-click Microsoft OneDrive and hit Disable in the context menu.
- Restart your computer and check that OneDrive does not start automatically.
Reset OneDrive
After resetting the settings, OneDrive should work as if this application had already been installed (similarly to the fresh installation).
You can reset OneDrive by running the command in CMD. Take into account the path where the OneDrive client is installed on your computer.
"%ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft OneDrive\onedrive.exe" /reset
If OneDrive has not started automatically in a few minutes after the reset, launch OneDrive manually.
Reinstall OneDrive
Sometimes reinstalling OneDrive can help resolve the slow performance issues of Microsoft OneDrive.
- Press Win+R, type
cmdand hit Enter to open the Windows command prompt. - Stop the running OneDrive process
taskkill /f /im OneDrive.exe - Run this command to uninstall OneDrive in Windows 64-bit. The path may differ for OneDrive versions. In our case, the command is:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft OneDrive\22.002.0103.0004\OneDriveSetup.exe" /uninstall - Download the latest OneDrive version from the Microsoft website and install it on your computer.
OneDrive is a cloud storage service for copying and synchronizing files. However, the OneDrive Sync client is not a backup solution. If you use OneDrive to backup files, and Microsoft OneDrive is slowing down your computer, consider using a dedicated data protection solution optimized for transferring large amounts of data and includes advanced features for data protection.
The general recommendation is to perform a OneDrive backup to avoid data loss. You can lose OneDrive data if someone accidentally deletes the data or if a computer is infected with ransomware and corrupted data is synchronized between a local disk and OneDrive cloud storage.
Other Recommendations to Fix Office 365 Issues
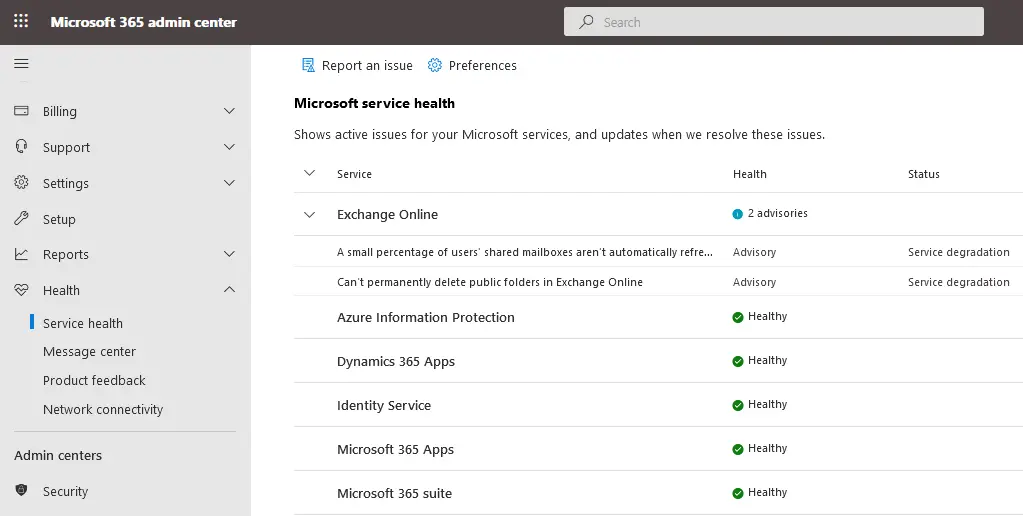
Issues on Microsoft servers occur rarely, but they are possible. In this situation, you can notice Office 365 slow performance due to issues on the server side. Check the Office 365 service health status for your account in the Office 365 admin center to verify whether all services on Microsoft’s cloud side are working properly.
- Open the Office 365 service health page in a web browser.
- Check that the All services tab is selected by default. A green icon under Current Health indicates that a service is working well. If you see a red icon, there may be service incidents at a datacenter on Microsoft’s side, which can be the reason for Office 365 slow performance.
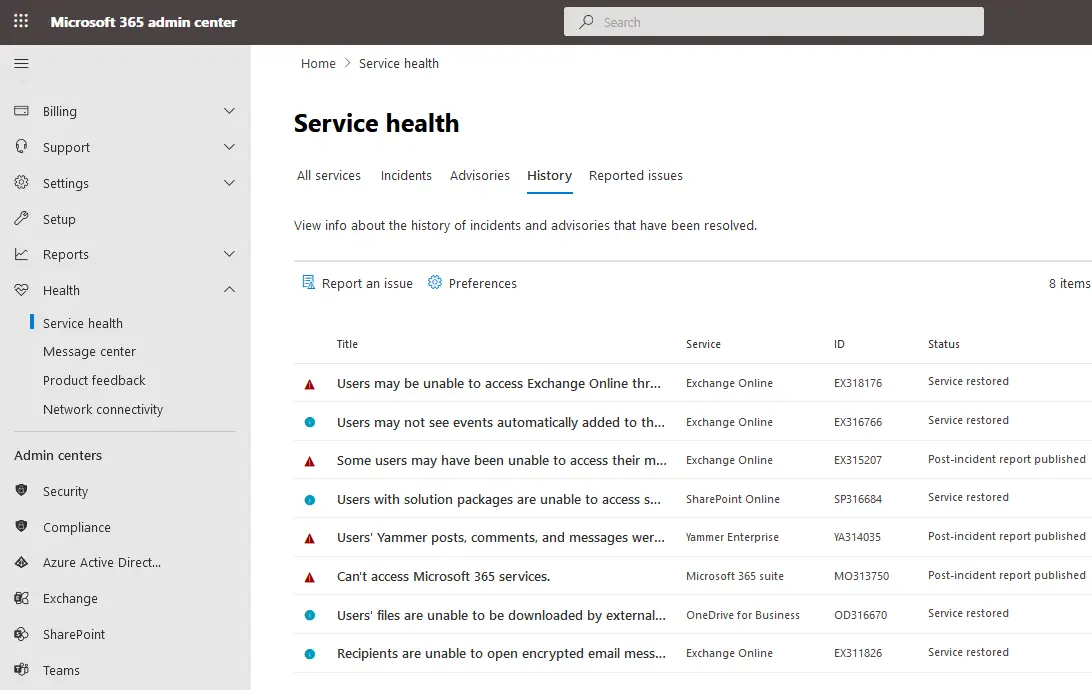
- Select the History tab on the Service Health page to see additional information about logged service interruptions and issues.
- You can also check the Office 365 network connectivity data page to identify Office 365 network connectivity issues.
- Additionally, you can check the Office 365 service health status on https://status.office.com
- Contact Microsoft technical support if any of the methods explained above didn’t help you resolve Office 365 problems related to performance.
Clear cache or temporary files
Each application stores cache or temporary data that may get corrupted. This can cause slow performance in Office 365. Delete the application cache to troubleshoot the issue.
- Outlook
Exit Outlook. Delete files in:
%localappdata%\Microsoft\Outlook\RoamCache
- Teams
Quit Teams. Delete everything in:
%appdata%\Microsoft\Teams\Cache
- Word/Excel/PowerPoint
Delete temp files in the %temp% folder (sort by date and remove Office-related files).
Analyzing log files for sync or latency Issues
If the reason for Office 365 slow performance is not apparent, checking and analyzing log files can help identify the problem. Log data can be useful, especially when identifying problems in Outlook, OneDrive, Microsoft Teams or other cloud-connected Office applications. Different applications and services generate logs in different locations.
Outlook – sync and connectivity logs
Log location in Outlook is in the Sync Issues folder (in Outlook itself). This item can be found under Mail Folders > Sync Issues.
To enable logging (if not enabled):
- Go to File > Options > Advanced.
- Under Other, check “Enable troubleshooting logging (requires restart)”.
The file path for log files:
%temp%\Outlook Logging\
%localappdata%\Microsoft\Outlook
Look for delayed or failed sync timestamps, repeated retries to Exchange or Microsoft 365 servers and error codes such as 0x800CCC0E, 0x8004010F, etc.
OneDrive – sync and latency logs
Log location is:
%localappdata%\Microsoft\OneDrive\logs
Important log files are:
UserTelemetryCache.otc
SyncDiagnostics.log
Business1.log
Look for repeated sync errors, files that fail to upload/download, throttling messages from SharePoint/OneDrive servers and error codes. “Error Code: 0x8004de40” indicates network/connectivity problems.
This can be useful for resolving issues like OneDrive not syncing or showing “Processing changes”.
Teams – sign-in and latency logs
Log location:
%appdata%\Microsoft\Teams\logs.txt
%appdata%\Microsoft\Teams\debug.log (and media-stack in the same directory)
To collect logs, right-click the Microsoft Teams icon in the system tray and hit Collect support files. This generates a .zip file with all logs for analysis.
Look for:
- Errors like ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED, ERR_CONNECTION_TIMED_OUT
- Delays or failures during login
- WebSocket connection errors (affect real-time comms)
- Latency between clients and Microsoft servers
Office 365 Performance Issues: System-Wide or App-Specific?
The nature of Office 365 (Microsoft 365) performance issues can be either system-wide or app-specific, depending on the root cause. Let’s explore how to determine system-wide issues from app-specific issues.
Symptoms of system-wide issues:
- All Office applications (Word, Excel, Outlook, Microsoft Teams) load slowly.
- Delayed response when switching between apps or typing.
- High CPU, RAM or disk usage when Microsoft Office is open.
- Frequent freezing or crashing across different applications.
Common causes:
- Low system resources (RAM/CPU/HDD issues).
- Windows OS problems or pending updates.
- Antivirus or security software scanning all Microsoft Office activity.
- Conflicts with other software running in the background.
- Corrupted Microsoft Office installation or shared services.
App-specific performance issues affect only one Office application, while others work fine.
Symptoms of app-specific issues:
- Outlook is slow to open or sync, but Word and Excel work fine.
- Excel freezes with large spreadsheets, but Word runs smoothly.
- Microsoft Teams has call quality issues, but other Office applications are unaffected.
Common causes:
- Add-ins or plugins specific to that app.
- Corrupted profiles (especially in Outlook or Microsoft Teams).
- App-specific settings or cache causing delays.
- Heavy workloads (for example, massive Excel formulas or Outlook mailboxes).
- Network issues affecting cloud-connected features (Outlook, OneDrive).
Identifying and resolving slowdowns in Office 365
To identify whether an Office 365 performance issue is app-specific or system-wide, consider the following tips:
- Open other Microsoft Office applications. If they’re also slow, it’s likely system-wide.
- Check the Task Manager. High CPU/memory usage may point to system-level resource strain.
- Run a Safe Mode test (such as Outlook /safe). If the application runs better, it’s likely an app-specific issue (add-in or config).
- Try another user profile. If the issue disappears, it’s likely app-specific or user-specific.
You can use Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant. This tool can automatically detect whether the problem is with a specific application or something broader.
Conclusion
Office 365 is an advanced cloud-based solution, but sometimes you may notice Office 365 slow performance. Now you know the common reasons for Microsoft Office 365 running slowly and possible methods to fix related issues. General issues and recommendations are related to the internet connection, hardware and software issues on the user’s computer. There are specific issues for particular Office 365 applications and tuning their settings can help you improve performance.




